comparing student loan options
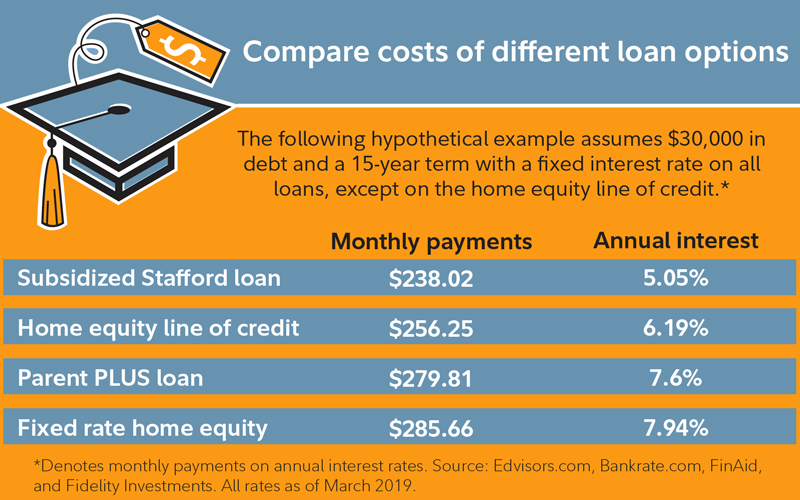
When it comes to financing higher education, student loans often become a necessary evil. With a plethora of options available, choosing the right student loan can be overwhelming. This comprehensive guide aims to simplify the process by comparing different student loan options, enabling you to make an informed decision that aligns with your financial goals.
Whether you are a prospective student or a parent seeking financial assistance for your child's education, understanding the nuances of various student loan options can save you from future financial burdens. From federal loans to private loans and everything in between, this article will delve into the details, benefits, and drawbacks of each option, helping you navigate through the complexities of the student loan landscape.
Federal Student Loans
When considering student loan options, federal loans are often the first choice for many borrowers. These loans are provided by the government and offer several benefits that make them attractive to students. There are three main types of federal student loans: Direct Subsidized Loans, Direct Unsubsidized Loans, and PLUS Loans.
Direct Subsidized Loans
Direct Subsidized Loans are available to undergraduate students with demonstrated financial need. The government pays the interest on these loans while the student is enrolled in school at least half-time, during the grace period, and during deferment periods. This means that the loan balance does not increase during these periods, making them an excellent option for financially disadvantaged students.
Direct Unsubsidized Loans
Direct Unsubsidized Loans are available to both undergraduate and graduate students, regardless of financial need. Unlike subsidized loans, interest accrues on unsubsidized loans from the time the loan is disbursed. However, students have the option to defer interest payments while in school, which means the interest is added to the loan balance. Despite this, unsubsidized loans are still a popular choice due to their availability to a wider range of students.
PLUS Loans
PLUS Loans are available to graduate students and parents of dependent undergraduate students. These loans can cover any remaining education expenses not covered by other financial aid. Unlike subsidized and unsubsidized loans, PLUS Loans require a credit check, and the borrower must not have an adverse credit history. PLUS Loans have higher interest rates compared to other federal loans but may still be a viable option for those who need additional funding.
Overall, federal student loans offer fixed interest rates, flexible repayment options, and various benefits such as loan forgiveness programs and income-driven repayment plans. They also come with borrower protections, such as deferment and forbearance options, that can provide temporary relief during financial difficulties.
Private Student Loans
While federal loans are the go-to choice for many, private student loans are an alternative option that should not be overlooked. Private loans are offered by banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions. Unlike federal loans, private loans require a credit check and often require a co-signer, especially for students with limited credit history or income.
Interest Rates and Terms
One of the main advantages of private student loans is the potential for lower interest rates, especially for borrowers with excellent credit scores. Private loans may also offer more flexible repayment terms, allowing borrowers to choose between fixed and variable interest rates, as well as various repayment plans.
Eligibility and Application Process
Private student loans have specific eligibility requirements set by the lender. These requirements may include factors such as credit history, income, and enrollment status. The application process for private loans typically involves submitting an application, providing documentation, and undergoing a credit check. It's essential to compare different lenders and their offerings to find the best terms and rates for your specific situation.
Considerations and Drawbacks
While private student loans can be beneficial for some borrowers, they also come with certain considerations and drawbacks. Private loans may have higher interest rates compared to federal loans, which can significantly increase the overall cost of borrowing. Additionally, private loans may not offer the same borrower protections and repayment options as federal loans, making it crucial to thoroughly understand the terms and conditions before committing to a private loan.
When deciding between federal and private student loans, it's essential to carefully consider your financial situation, future earning potential, and long-term goals. Exploring both options and comparing the benefits and drawbacks will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your specific needs.
Income-Driven Repayment Plans
For borrowers who anticipate challenges in repaying their student loans, income-driven repayment plans can offer relief. Income-driven repayment plans tie the monthly loan payment amount to the borrower's income and family size, ensuring that the payment is manageable based on their financial circumstances.
How Income-Driven Repayment Plans Work
Income-driven repayment plans calculate the monthly payment amount by considering a percentage of the borrower's discretionary income. The discretionary income is determined by subtracting a percentage of the federal poverty guideline from the borrower's adjusted gross income. The resulting amount is then multiplied by the chosen percentage associated with the specific income-driven repayment plan.
Types of Income-Driven Repayment Plans
There are several types of income-driven repayment plans available, including Income-Based Repayment (IBR), Pay As You Earn (PAYE), Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE), and Income-Contingent Repayment (ICR). Each plan has its own eligibility requirements, calculation methods, and repayment terms.
Benefits and Drawbacks
Income-driven repayment plans offer several benefits, such as potentially lower monthly payments, loan forgiveness after a certain period of time, and the ability to adjust payments based on income changes. These plans can be particularly advantageous for borrowers with high debt-to-income ratios or those pursuing careers with lower income potential.
However, it's important to consider the potential drawbacks of income-driven repayment plans as well. Extending the repayment period through these plans may result in paying more interest over the life of the loan. Additionally, forgiven loan amounts under income-driven plans may be considered taxable income, potentially resulting in a tax liability.
Loan Consolidation
If you have multiple student loans, consolidating them into a single loan can simplify the repayment process and potentially save you money. Loan consolidation allows you to combine your existing loans into a new loan with a single monthly payment.
Benefits of Loan Consolidation
Consolidating your student loans can provide several advantages. First, it simplifies repayment by consolidating multiple loans into one, reducing the hassle of managing multiple payments and due dates. It can also help you secure a fixed interest rate, which can provide stability and potentially save you money if interest rates rise in the future.
Considerations and Drawbacks
While loan consolidation can be beneficial, it's important to consider certain factors before proceeding. Consolidating federal loans with private loans may result in losing specific federal loan benefits, such as loan forgiveness programs and income-driven repayment options. Additionally, extending the repayment period through consolidation may result in paying more interest over time, even if the monthly payment amount is reduced.
Loan Forgiveness Programs
Loan forgiveness programs offer a way for borrowers to have a portion or the entirety of their student loans forgiven, typically in exchange for working in specific professions or for certain employers. These programs can provide significant financial relief for eligible borrowers.
Types of Loan Forgiveness Programs
Several loan forgiveness programs are available, each with its own eligibility criteria and requirements. Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) is a popular program that forgives the remaining loan balance for borrowers who work full-time for qualifying employers in the public sector. Teacher Loan Forgiveness is another program that offers forgiveness for teachers who work in low-income schools for a specified period.
Eligibility and Application Process
Eligibility for loan forgiveness programs varies depending on the specific program. Generally, borrowers must meet certain criteria, such as working in qualifying professions or for eligible employers for a specified period. Each program has its own application process, which typically involves submitting documentation and meeting specific requirements.
Benefits and Considerations
Loan forgiveness programs provide significant benefits by helping borrowers eliminate their student loan debt. However, it's important to consider the potential drawbacks and limitations of these programs. Some forgiveness programs have strict eligibility requirements and may require borrowers to make consistent payments for a specified period before becoming eligible for forgiveness. Additionally, forgiven loan amounts may be considered taxable income, resulting in a potential tax liability.
Interest Rates and Fees
Understanding interest rates and fees associated with different student loan options is crucial when comparing loan options. Interest rates determine the cost of borrowing and can significantly impact the overall repayment amount.
Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rates
Student loans can have either fixed or variable interest rates. Fixed interest rates remain the same throughout the life of the loan, providing stability and predictability in monthly payments. Variable interest rates, on the other hand, can fluctuate over time based on changes in the market. While variable rates may initially be lower, they can increase over time, potentially resulting in higher overall costs.
Origination Fees and Other Charges
In addition to interest rates, it's essential to consider any origination fees or other charges associated with student loans. Orig
Origination Fees and Other Charges
In addition to interest rates, it's essential to consider any origination fees or other charges associated with student loans. Origination fees are upfront fees charged by lenders to cover the cost of processing the loan. These fees are typically a percentage of the loan amount and are deducted from the loan disbursement. Some loans may also have other charges, such as late payment fees or prepayment penalties. Understanding these fees and charges will give you a clearer picture of the overall cost of borrowing.
Comparing Interest Rates and Fees
When comparing student loan options, it's important to consider both the interest rates and fees associated with each loan. While a loan with a lower interest rate may initially seem more attractive, it's crucial to factor in any fees and charges that may significantly impact the overall cost of borrowing. By comparing the APR (annual percentage rate) of different loans, which includes both the interest rate and fees, you can make a more informed decision about which loan is the most cost-effective.
Repayment Options and Terms
Understanding the repayment options and terms of your student loans is essential for managing your debt effectively and avoiding financial difficulties in the future. Different repayment plans offer flexibility in terms of monthly payments and the overall duration of the repayment period.
Standard Repayment Plan
The standard repayment plan is the default option offered by most lenders. Under this plan, borrowers make fixed monthly payments over a set period, usually ten years. This plan typically results in higher monthly payments but allows borrowers to pay off their loans faster and save on interest over time.
Extended Repayment Plan
The extended repayment plan offers borrowers a longer repayment period, typically up to 25 years. This plan can lower monthly payments by stretching them out over a more extended period. However, it's important to note that while this may provide temporary relief, it may also result in paying more interest over the life of the loan.
Graduated Repayment Plan
The graduated repayment plan starts with lower monthly payments that gradually increase over time. This plan is suitable for borrowers who anticipate an increase in their income over the years. While the initial payments may be more manageable, it's important to consider the potential impact of higher payments in the future.
Income-Driven Repayment Plans
As mentioned earlier, income-driven repayment plans tie monthly payments to the borrower's income and family size. These plans offer flexibility by adjusting payments based on the borrower's financial circumstances. Income-driven plans include options such as Income-Based Repayment (IBR), Pay As You Earn (PAYE), Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE), and Income-Contingent Repayment (ICR).
Deferment and Forbearance
In certain situations, borrowers may be eligible for deferment or forbearance, which allow them to temporarily suspend or reduce their loan payments. Deferment is typically granted for specific circumstances such as enrollment in school, unemployment, or economic hardship. Forbearance, on the other hand, is a temporary reduction or suspension of payments granted at the lender's discretion. It's important to note that interest may continue to accrue during deferment or forbearance, potentially increasing the overall cost of the loan.
Loan Default and Its Consequences
Defaulting on student loans can have severe consequences, including damage to your credit score and financial stability. Default occurs when a borrower fails to make payments for an extended period, typically 270 days or more. It's crucial to understand the potential consequences of default and take steps to avoid it.
Impact on Credit Score
Defaulting on student loans can significantly damage your credit score, making it challenging to secure future loans or obtain favorable interest rates. A lower credit score can also impact other aspects of your financial life, such as renting an apartment or obtaining insurance.
Wage Garnishment and Legal Actions
In cases of default, lenders have the right to take legal action to recover the outstanding loan balance. This may include wage garnishment, where a portion of your wages is withheld to repay the debt. Legal actions can result in additional legal fees and expenses, further exacerbating your financial situation.
Rehabilitation and Loan Consolidation
If you find yourself in default, there are options available to rehabilitate your loans and get back on track. Loan rehabilitation programs allow borrowers to make a series of consecutive, voluntary, and reasonable payments to bring the loans out of default. Loan consolidation is another option where you can combine your defaulted loans into a new loan with a new repayment plan.
Borrower Protections and Rights
As a borrower, you have certain rights and protections when it comes to student loans. Understanding these rights can help you navigate the loan repayment process and ensure that you are treated fairly by lenders.
Loan Discharge in Special Circumstances
In certain situations, borrowers may be eligible for loan discharge, where the loan balance is forgiven or canceled. These special circumstances include total and permanent disability, death, closure of the school attended, or false certification by the school.
Deferment and Forbearance Options
As mentioned earlier, deferment and forbearance options can provide temporary relief for borrowers facing financial hardships. It's important to understand the eligibility criteria and processes for obtaining deferment or forbearance and to communicate with your loan servicer to explore these options when needed.
Loan Servicer Responsibilities
Your loan servicer plays a vital role in managing your student loans. They are responsible for collecting payments, providing information about repayment options, and assisting you throughout the loan repayment process. It's important to stay in contact with your loan servicer and promptly address any issues or concerns that may arise.
Tips for Paying Off Student Loans Faster
While student loans can be a significant financial burden, there are strategies you can employ to pay them off faster and reduce the overall cost of borrowing. By taking proactive steps, you can accelerate your journey to becoming debt-free.
Create a Budget and Cut Expenses
Creating a budget allows you to track your income and expenses and identify areas where you can cut back. By minimizing unnecessary expenses and redirecting those funds towards your student loan payments, you can make substantial progress towards paying off your loans faster.
Make Extra Payments
Making extra payments towards your student loans, even if it's just a little more than the minimum required payment, can have a significant impact. By allocating additional funds towards the principal balance, you can reduce the amount of interest accrued over time and shorten the overall repayment period.
Consider Loan Refinancing
Loan refinancing involves replacing your current loans with a new loan that offers better terms, such as a lower interest rate. Refinancing can help you save money on interest and potentially reduce your monthly payments, allowing you to pay off your loans more efficiently. However, it's important to carefully evaluate the terms and fees associated with refinancing before making a decision.
Take Advantage of Employer-Sponsored Repayment Programs
Some employers offer student loan repayment assistance as part of their benefits package. This can include direct payments towards your loans or matching contributions. If your employer offers such a program, take advantage of it to accelerate your repayment journey.
Explore Loan Forgiveness and Repayment Assistance Programs
As mentioned earlier, loan forgiveness programs exist for borrowers working in certain professions or for qualifying employers. Research and explore these programs to see if you qualify. Additionally, some states and organizations offer repayment assistance programs that provide financial incentives for borrowers working in specific fields or underserved areas.
Choosing the right student loan is a decision that can have a lasting impact on your financial future. By comparing and understanding the various student loan options available, you can make an informed choice that aligns with your unique circumstances.
Remember, it's essential to consider factors such as interest rates, repayment options, and borrower protections when evaluating student loan options. This comprehensive guide has equipped you with the knowledge necessary to navigate the complex world of student loans confidently.
Take the time to weigh the pros and cons of each option, assess your financial capabilities, and carefully plan your repayment strategy. With proper research and planning, you can embark on your educational journey without being burdened by overwhelming student loan debt.
0 Response to "comparing student loan options"
Posting Komentar